Diabetes Risk Screening in Dental Practices
BY Total Health Screens – 4 years ago
As an organisation we are on a mission to empower dentistry to support patients with oral and overall health. Dental professionals see more patients than almost any other healthcare providers and we can really make a difference for both the patient and our healthcare system.
This year marks 100 years since the discovery of insulin, a treatment that has saved millions of lives around the world.
Let’s look back a few years from now and show how dentistry has helped millions with the detection, prevention and education of diabetes and how oral health is linked.
1 million people in the UK have undiagnosed type 2 diabetes.
–
Let’s work together to keep this number from rising!

What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces.
What is the link between diabetes and oral health?
With increased blood glucose levels, people living with diabetes may have more glucose in their saliva and very dry mouths. These conditions allow dental plaque to build up on teeth, which leads to tooth decay and cavities.
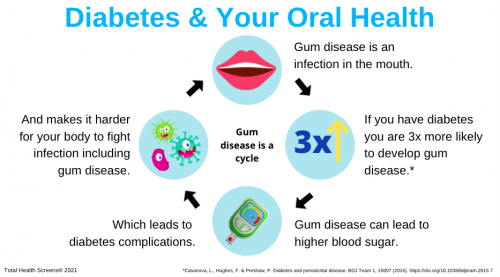
Does diabetes increase risk of gum disease?
Diabetes that is not controlled well leads to higher blood sugar (glucose) levels in the mouth fluids. This promotes the growth of bacteria that can cause gum disease.
Periodontitis is a progressive bacterial infection within the gum tissue that if neglected, can severely damage or destroy your gums, teeth, and jaw. However, like any infection, gum disease may profoundly affect and destabilise you’re the blood glucose level, therefore making them increasingly difficult to control and ultimately allowing the diabetes to exponentially progress.
What are the two types of diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (formerly called non-insulin-dependent, or adult-onset) results from the body’s ineffective use of insulin. The majority of people with diabetes have type 2 diabetes. This type of diabetes is largely the result of excess body weight and physical inactivity.
Symptoms may be similar to those of type 1 diabetes, but are often less marked. As a result, the disease may be diagnosed several years after onset, after complications have already arisen.
Until recently, this type of diabetes was seen only in adults but it is now also occurring increasingly frequently in children.
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (previously known as insulin-dependent, juvenile or childhood-onset) is characterised by deficient insulin production and requires daily administration of insulin. Neither the cause of Type 1 diabetes nor the means to prevent it are known.
Symptoms include excessive excretion of urine (polyuria), thirst (polydipsia), constant hunger, weight loss, vision changes, and fatigue. These symptoms may occur suddenly.
Possible Warning Signs
Symptoms of diabetes can affect all aspects of your health. However, if left unchecked, they can almost immediately begin to affect your oral health. Some of the telltale symptoms are:
• Frequent bouts of thirst and or dry mouth
• Swollen or bleeding gums
• Difficulty tasting certain foods
• Prolonged or slow-healing sores or wounds
• Increased susceptibility to additional oral infections or complications
Dental professionals are healthcare providers.
1 – Share information with your patients about diabetes and the link between oral health. Free Download Link Between Diabetes & Oral Health.pdf
2 – Offer a simple diabetes risk screen that only takes minutes schedule a call to deliver diabetes and other health screens.
3 – Have fun sharing diabetes awareness with your patients, take part in the #NailingDiabetes challenge and help us nail a cure. On 14 November, paint your nails blue to raise awareness of diabetes.


